Mark Levin, a prominent American lawyer, author, and radio personality, has made significant contributions to the political landscape through his insightful commentary and literary works. With a career spanning several decades, Levin has garnered a dedicated following, becoming a household name in conservative circles. However, beyond his professional achievements, Levin's personal journey includes navigating the challenges of Parkinson's disease, a neurodegenerative disorder that affects millions worldwide.
Parkinson's disease is characterized by a progressive decline in motor and non-motor functions, leading to a range of symptoms that can significantly impact an individual's quality of life. As Levin continues to share his experiences, his story serves as a beacon of hope for others facing similar health challenges. His openness about his condition sheds light on the importance of awareness, early diagnosis, and effective treatment strategies.
This article delves into Mark Levin's Parkinson's disease journey, exploring the symptoms, diagnostic processes, and treatment options available. By examining Levin's experiences, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of Parkinson's disease, offering valuable insights for patients, caregivers, and medical professionals alike. Join us as we uncover the intricacies of this complex condition and the resilience displayed by one of America's most influential voices.
Table of Contents
- Mark Levin: A Brief Biography
- Personal Details and Bio Data
- What is Parkinson's Disease?
- How Does Parkinson's Disease Affect the Body?
- Early Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease
- Advanced Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease
- Mark Levin's Parkinson's Disease Journey
- How is Parkinson's Disease Diagnosed?
- Treatment Options for Parkinson's Disease
- Medication for Parkinson's Disease
- Surgical Interventions for Parkinson's Disease
- Lifestyle Changes and Therapies
- Support and Coping Strategies
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Mark Levin: A Brief Biography
Mark Reed Levin, born on September 21, 1957, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, is a distinguished figure in American media and politics. Levin's career is marked by his accomplishments in law, literature, and broadcasting, contributing significantly to conservative discourse in the United States. A graduate of Temple University Beasley School of Law, Levin began his professional journey as an attorney, eventually serving in the Reagan administration as Chief of Staff to Attorney General Edwin Meese.
Levin's transition into media was marked by his tenure as a radio host, where he gained recognition for his incisive political commentary on "The Mark Levin Show." His literary contributions include several bestselling books, such as "Liberty and Tyranny" and "American Marxism," which have resonated with audiences across the nation. Despite his professional success, Levin's personal life took a challenging turn with his Parkinson's disease diagnosis, a journey he has openly shared with the public.
Personal Details and Bio Data
| Full Name | Mark Reed Levin |
|---|---|
| Date of Birth | September 21, 1957 |
| Birthplace | Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA |
| Education | Temple University Beasley School of Law |
| Profession | Lawyer, Author, Radio Host |
| Notable Works | "Liberty and Tyranny," "American Marxism" |
| Diagnosis | Parkinson's Disease |
What is Parkinson's Disease?
Parkinson's disease is a chronic and progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects movement. It is characterized by the gradual degeneration of nerve cells in the brain, particularly those in the substantia nigra, a region responsible for producing dopamine. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter crucial for coordinating smooth and controlled muscle movements. As dopamine levels decrease, individuals with Parkinson's disease experience a range of motor and non-motor symptoms that can vary in severity and progression.
While the exact cause of Parkinson's disease remains unknown, it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Researchers have identified several genes associated with an increased risk of developing the condition, but the majority of Parkinson's cases are sporadic, meaning they occur without a clear familial link. Environmental factors, such as exposure to certain toxins and head injuries, may also contribute to the development of the disease.
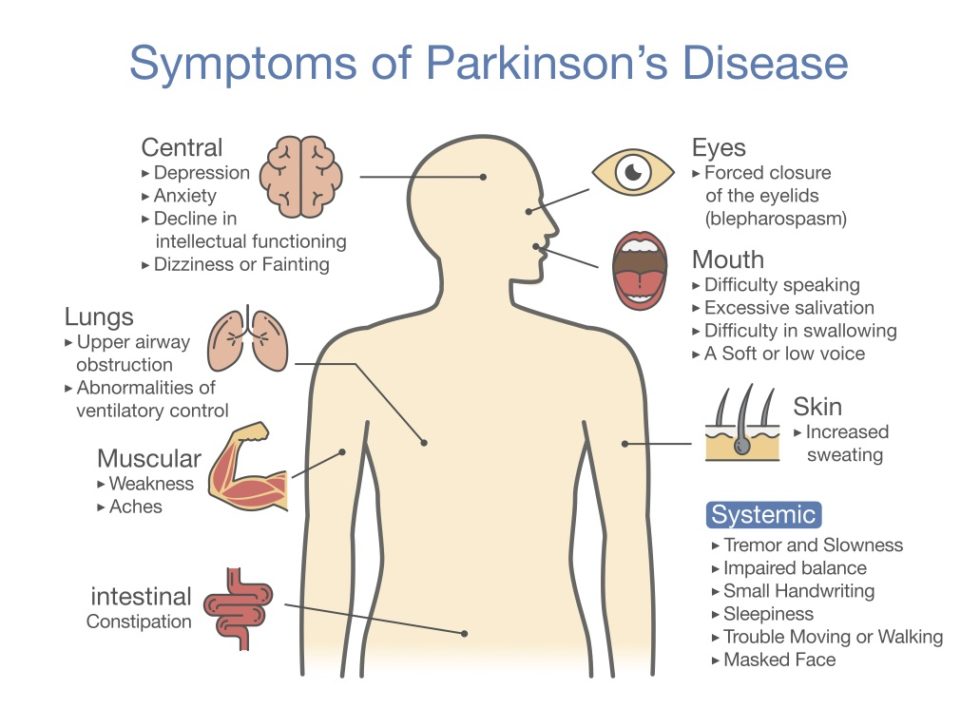
How Does Parkinson's Disease Affect the Body?
Parkinson's disease primarily affects the central nervous system, leading to a range of symptoms that can impact both physical and cognitive functions. The most recognizable symptoms are motor-related, including tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia (slowness of movement), and postural instability. These symptoms can make everyday tasks challenging and may lead to difficulties with balance, coordination, and speech.
In addition to motor symptoms, Parkinson's disease can also manifest through non-motor symptoms, which may include:
- Depression and anxiety
- Sleep disturbances
- Cognitive impairment
- Autonomic dysfunction (e.g., constipation, urinary problems)
- Olfactory dysfunction (loss of sense of smell)
The progression of Parkinson's disease varies from person to person, with some individuals experiencing a slow decline in function while others may face more rapid changes. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial in managing the symptoms and improving the quality of life for those affected.
Early Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease
Recognizing the early symptoms of Parkinson's disease is essential for timely diagnosis and intervention. In its initial stages, the disease may present with subtle signs that are often overlooked or attributed to normal aging. Some of the early symptoms include:
- Tremors: Involuntary shaking or trembling, usually starting in the hands or fingers, is one of the hallmark symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
- Bradykinesia: A noticeable slowing of movement, making simple tasks take longer to complete.
- Rigidity: Stiffness or inflexibility of the limbs and joints, often accompanied by muscle pain or discomfort.
- Postural instability: Difficulty maintaining balance or making quick movements, leading to an increased risk of falls.
- Changes in facial expression: A reduction in spontaneous facial movements, resulting in a masked or expressionless appearance.
- Micrographia: Small, cramped handwriting that may worsen over time.
In addition to these motor symptoms, individuals with Parkinson's disease may also experience early non-motor symptoms such as:
- Loss of smell
- Constipation
- Sleep disturbances
- Mood changes (e.g., depression, anxiety)
These early signs may precede motor symptoms by several years, highlighting the importance of comprehensive medical evaluation for individuals experiencing these changes.
Advanced Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease
As Parkinson's disease progresses, the symptoms become more pronounced and may significantly impact an individual's daily life. Advanced symptoms can include a combination of severe motor and non-motor manifestations, such as:
- Severe tremors: Persistent shaking that affects multiple parts of the body, making it difficult to perform daily activities.
- Postural instability: Increased difficulty maintaining balance, leading to frequent falls and injuries.
- Freezing of gait: A sudden, temporary inability to move or initiate walking, causing episodes of "freezing."
- Dyskinesia: Involuntary, erratic movements resulting from long-term use of dopaminergic medications.
- Cognitive impairment: Difficulties with memory, concentration, and problem-solving, potentially leading to dementia.
- Autonomic dysfunction: Problems with blood pressure regulation, temperature control, and bladder and bowel function.
Advanced non-motor symptoms may also include:
- Severe depression and anxiety
- Sleep disorders, such as vivid dreams or REM sleep behavior disorder
- Hallucinations and delusions
- Loss of motivation and apathy
The progression of these symptoms can vary widely among individuals, emphasizing the need for personalized treatment plans and ongoing medical support.
Mark Levin's Parkinson's Disease Journey
Mark Levin's battle with Parkinson's disease is a testament to his resilience and determination. After his diagnosis, Levin has been candid about his experiences, using his platform to raise awareness about the condition and its impact on daily life. His journey highlights the importance of recognizing early symptoms and seeking prompt medical attention to manage the disease effectively.
Levin's symptoms, which include tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia, have been managed through a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and support from his family and healthcare team. His openness about his condition has inspired many to seek information and support, fostering a sense of community among those affected by Parkinson's disease.
How is Parkinson's Disease Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Parkinson's disease can be challenging, as there is no definitive test for the condition. Instead, healthcare professionals rely on a combination of clinical evaluation, medical history, and diagnostic tests to identify the presence of the disease. The diagnostic process typically involves:
- Neurological examination: A thorough assessment of motor functions, reflexes, coordination, and balance.
- Medical history review: An evaluation of the patient's symptoms, family history, and any potential risk factors.
- Imaging tests: While not definitive, brain imaging techniques such as MRI or PET scans can help rule out other conditions with similar symptoms.
- Response to medication: A trial of dopaminergic medication, such as levodopa, may be used to assess symptom improvement, supporting a Parkinson's diagnosis.
In some cases, additional tests, such as genetic testing or specialized imaging studies, may be conducted to further evaluate the condition. Early diagnosis is crucial for implementing effective treatment strategies and improving outcomes for individuals with Parkinson's disease.
Treatment Options for Parkinson's Disease
While there is currently no cure for Parkinson's disease, a range of treatment options is available to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment plans are tailored to each individual's needs and may include a combination of medication, surgery, and lifestyle modifications. Key treatment strategies include:
Medication for Parkinson's Disease
Medications play a central role in managing Parkinson's disease symptoms. The goal is to increase dopamine levels in the brain or mimic its effects to improve motor function. Common medications include:
- Levodopa: A precursor to dopamine that is converted into the neurotransmitter in the brain, helping to alleviate symptoms like bradykinesia and rigidity.
- Dopamine agonists: Drugs that mimic dopamine's effects, such as pramipexole and ropinirole, used to manage symptoms and reduce "off" periods.
- MAO-B inhibitors: Medications that block the breakdown of dopamine in the brain, prolonging its effects.
- COMT inhibitors: Drugs that prevent the breakdown of levodopa, extending its duration of action.
Medications are often combined to achieve optimal symptom control, and healthcare providers regularly adjust dosages to manage side effects and ensure efficacy.
Surgical Interventions for Parkinson's Disease
For individuals with advanced Parkinson's disease or those who do not respond well to medication, surgical interventions may be considered. The most common procedure is Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS), which involves implanting electrodes in specific brain regions to regulate abnormal electrical signals. DBS can help reduce tremors, improve motor symptoms, and decrease medication requirements.
Other surgical options, such as pallidotomy or thalamotomy, are less commonly performed but may be considered for specific cases. These procedures involve destroying small areas of brain tissue to alleviate symptoms.
Lifestyle Changes and Therapies
In addition to medical and surgical treatments, lifestyle changes and supportive therapies are essential components of Parkinson's disease management. These strategies aim to enhance overall well-being and reduce symptom severity. Key approaches include:
- Physical therapy: Exercises and stretches to improve mobility, balance, and flexibility, reducing the risk of falls and enhancing daily function.
- Occupational therapy: Techniques to assist with daily activities and improve independence through adaptive strategies and equipment.
- Speech therapy: Interventions to address speech and swallowing difficulties, enhancing communication and nutritional intake.
- Diet and nutrition: A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, fiber, and nutrients to support overall health and manage non-motor symptoms.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity to boost cardiovascular health, increase strength, and alleviate depression and anxiety.
These lifestyle modifications, combined with medical treatment, can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with Parkinson's disease.
Support and Coping Strategies
Coping with Parkinson's disease requires a comprehensive support system that includes family, friends, healthcare professionals, and support groups. Emotional and social support is vital in managing the psychological impact of the disease and maintaining a positive outlook. Strategies for coping with Parkinson's disease include:
- Joining support groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges can provide a sense of community, shared experiences, and valuable information.
- Maintaining open communication: Discussing feelings and concerns with loved ones and healthcare providers to ensure a supportive environment.
- Seeking professional counseling: Therapy or counseling to address emotional and mental health challenges, such as depression and anxiety.
- Setting realistic goals: Establishing achievable objectives to maintain independence and foster a sense of accomplishment.
- Staying informed: Keeping up-to-date with the latest research and treatment options to make informed decisions about care and management.
By incorporating these strategies, individuals with Parkinson's disease can better navigate the challenges of the condition and lead fulfilling lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key symptoms of Parkinson's disease?
Key symptoms of Parkinson's disease include tremors, bradykinesia (slowness of movement), rigidity, and postural instability. Non-motor symptoms may include depression, sleep disturbances, and cognitive impairment.
How is Parkinson's disease diagnosed?
Parkinson's disease is diagnosed through a combination of clinical evaluation, medical history review, and diagnostic tests such as MRI or PET scans. There is no definitive test for Parkinson's, so diagnosis is based on symptom presentation and response to medication.
What treatment options are available for Parkinson's disease?
Treatment options for Parkinson's disease include medications, such as levodopa and dopamine agonists, surgical interventions like Deep Brain Stimulation, and lifestyle changes, including physical therapy and exercise.
Can lifestyle changes help manage Parkinson's symptoms?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and supportive therapies like physical and occupational therapy can help manage Parkinson's symptoms and improve quality of life.
Is there a cure for Parkinson's disease?
Currently, there is no cure for Parkinson's disease. However, various treatments and therapies can manage symptoms and enhance the quality of life for individuals living with the condition.
How does Mark Levin manage his Parkinson's disease?
Mark Levin manages his Parkinson's disease through a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and support from his healthcare team and family. His openness about his journey has inspired many to seek information and support.
Conclusion
Mark Levin's journey with Parkinson's disease underscores the importance of awareness, early diagnosis, and comprehensive treatment strategies in managing this complex neurological disorder. Through his public discourse and personal resilience, Levin has become a beacon of hope for those facing similar challenges, advocating for greater understanding and support for individuals with Parkinson's disease.
As we continue to explore the intricacies of Parkinson's disease and its impact on individuals like Levin, it is crucial to foster a supportive environment that encourages research, innovation, and community engagement. By doing so, we can work towards improving the lives of those affected by this condition and ultimately find a cure.
For more information on Parkinson's disease and support resources, visit reputable organizations such as the Michael J. Fox Foundation (https://www.michaeljfox.org/).